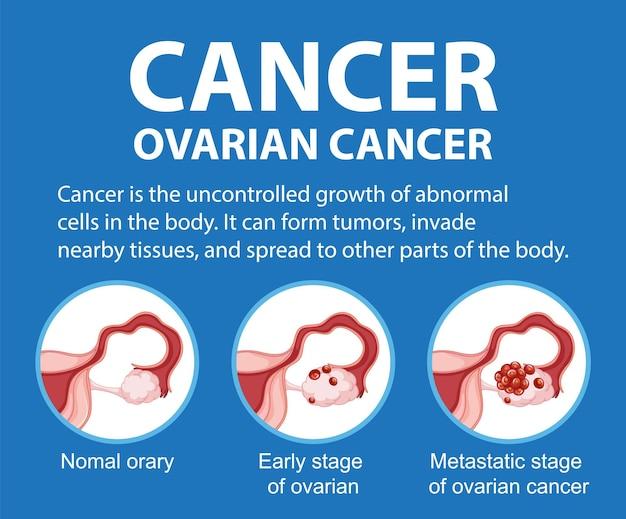
What is ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease that primarily affects women. It occurs when abnormal cells in the ovaries, the reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs and hormones, grow uncontrollably. Ovarian cancer can develop in different parts of the ovaries, including the epithelial cells that line the surface, the stromal cells that produce hormones, or the germ cells that develop into eggs.
While the exact cause of ovarian cancer is unknown, certain risk factors have been identified. Genetic mutations, family history of ovarian or breast cancer, age, reproductive history, hormone replacement therapy, and obesity are all factors that may increase the risk of developing ovarian cancer. Understanding these risk factors can help women take proactive steps towards prevention and early detection.
Risk factors for ovarian cancer
Several factors can increase a woman’s risk of developing ovarian cancer. One of the most significant risk factors is a family history of the disease. Women with close relatives, such as a mother, sister, or daughter, who have had ovarian cancer are at a higher risk. Additionally, certain genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations, significantly increase the likelihood of developing ovarian cancer.
Age also plays a crucial role, with the risk increasing as women get older. Most cases of ovarian cancer occur after menopause, but it can affect women of all ages. Women who have never been pregnant or who have had trouble getting pregnant may also have a slightly higher risk. Other risk factors include the use of hormone replacement therapy, obesity, and a personal history of breast, colorectal, or endometrial cancer.
Common symptoms of ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is often referred to as the “silent killer” because its symptoms are often vague and easily overlooked. However, being aware of these symptoms can help in early detection and improved treatment outcomes. Some common symptoms of ovarian cancer include:
Persistent bloating: Feeling bloated, especially if it lasts for more than a few weeks, can be a cause for concern. It is essential to distinguish between occasional bloating and persistent bloating that does not go away.
Abdominal or pelvic pain: Women with ovarian cancer may experience pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis. The pain may be constant or come and go.
Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly: A loss of appetite or feeling full after eating only a small amount can be a symptom of ovarian cancer. This occurs when the tumor affects the digestive system.
Changes in bowel habits: Ovarian cancer can cause changes in bowel movements, such as constipation or diarrhea, that are not related to other known conditions.
Unexplained weight loss: Sudden and unexplained weight loss can be a sign of various underlying health issues, including ovarian cancer.
It is important to note that these symptoms are not exclusive to ovarian cancer and can be caused by other conditions. However, if any of these symptoms persist and are not normal for you, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Early detection and diagnosis of ovarian cancer
Early detection plays a crucial role in successfully treating ovarian cancer. Unfortunately, due to its nonspecific symptoms, the disease is often diagnosed at later stages when it has spread beyond the ovaries. However, several diagnostic procedures can aid in the early detection and diagnosis of ovarian cancer.
Imaging tests: Ultrasound, transvaginal ultrasound, and computed tomography (CT) scans are commonly used imaging tests to visualize the ovaries and identify any abnormalities.
Blood tests: The CA-125 blood test measures the levels of a protein called CA-125, which is often elevated in women with ovarian cancer. While this test is not specific to ovarian cancer and can be elevated in other conditions, it may be used in combination with other diagnostic methods.
Biopsy: A biopsy involves removing a small tissue sample from the ovaries or surrounding tissues and examining it under a microscope to determine if cancer cells are present. This is usually done during surgery, such as a laparoscopy or laparotomy.
It is crucial to discuss any concerning symptoms with a healthcare professional who can evaluate the need for further diagnostic tests. Early detection can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment and long-term survival.
Different types and stages of ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is classified into different types based on the cells where it originates. The three main types are epithelial tumors, which begin in the cells that cover the outer surface of the ovaries; stromal tumors, which develop in the cells that produce hormones; and germ cell tumors, which arise from the cells that produce eggs.
Each type of ovarian cancer can also be further classified into stages, which determine the extent of the disease and guide treatment decisions. The stages range from stage 1, where the cancer is confined to the ovaries, to stage 4, where it has spread to distant organs.
Understanding the type and stage of ovarian cancer is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific characteristics and needs of the individual.
Treatment options for ovarian cancer
The treatment of ovarian cancer depends on various factors, including the type and stage of the disease, the overall health of the patient, and their preferences. The primary treatment options for ovarian cancer include surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies.
Surgery: Surgery is often the first line of treatment for ovarian cancer. The goal of surgery is to remove as much of the cancerous tissue as possible. This may involve removing the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, lymph nodes, and surrounding tissues. In some cases, a complete hysterectomy may be necessary.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It may be given before surgery to shrink the tumor, after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells, or as the primary treatment for advanced or recurrent ovarian cancer.
Targeted therapies: Targeted therapies are medications that specifically target cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells. These therapies work by interfering with specific molecules or pathways that are involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Other treatment options, such as radiation therapy and hormone therapy, may be used in specific cases. It is crucial for patients to work closely with their healthcare team to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for their individual situation.
Supportive care and managing side effects during treatment
Receiving a diagnosis of ovarian cancer and undergoing treatment can be physically and emotionally challenging. Alongside the primary treatment, supportive care plays a vital role in improving the quality of life for patients with ovarian cancer. Supportive care focuses on managing the side effects of treatment and addressing the emotional and psychological needs of patients.
Common side effects of ovarian cancer treatment include nausea, fatigue, hair loss, loss of appetite, and emotional distress. Supportive care measures, such as anti-nausea medications, pain management, nutritional support, and counseling, can help alleviate these side effects and improve overall well-being.
Additionally, complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, and yoga, can provide relaxation and reduce stress during treatment. It is essential for patients to communicate openly with their healthcare team about any side effects they are experiencing to ensure the appropriate supportive care measures are put in place.
Ovarian cancer survivor stories and inspirational resources
Hearing from other ovarian cancer survivors can provide hope, inspiration, and valuable insights into the journey of living with and overcoming the disease. Many organizations and online communities offer platforms for survivors to share their stories and connect with others who have had similar experiences.
In addition to survivor stories, there are various resources available to support individuals affected by ovarian cancer. Support groups, counseling services, educational materials, and online forums can provide information, emotional support, and a sense of community for patients, caregivers, and loved ones.
Ovarian cancer research and ongoing clinical trials
Ongoing research and clinical trials play a vital role in advancing the understanding and treatment of ovarian cancer. Clinical trials provide an opportunity for patients to access innovative treatments and contribute to scientific knowledge. Participating in a clinical trial should be done under the guidance of healthcare professionals, who can evaluate the potential benefits and risks.
It is important for patients and their loved ones to stay informed about the latest developments in ovarian cancer research and discuss any potential research opportunities with their healthcare team. By actively engaging in research, patients can potentially benefit from cutting-edge treatments and contribute to the future of ovarian cancer care.